Silicon metal is an essential material used in various industries, including electronics, solar energy, and aluminum production. The process of producing high-purity silicon metal involves several key steps, starting from the raw material extraction to the final refinement. Here’s an overview of how silicon metal is produced:

1. Raw Material Extraction
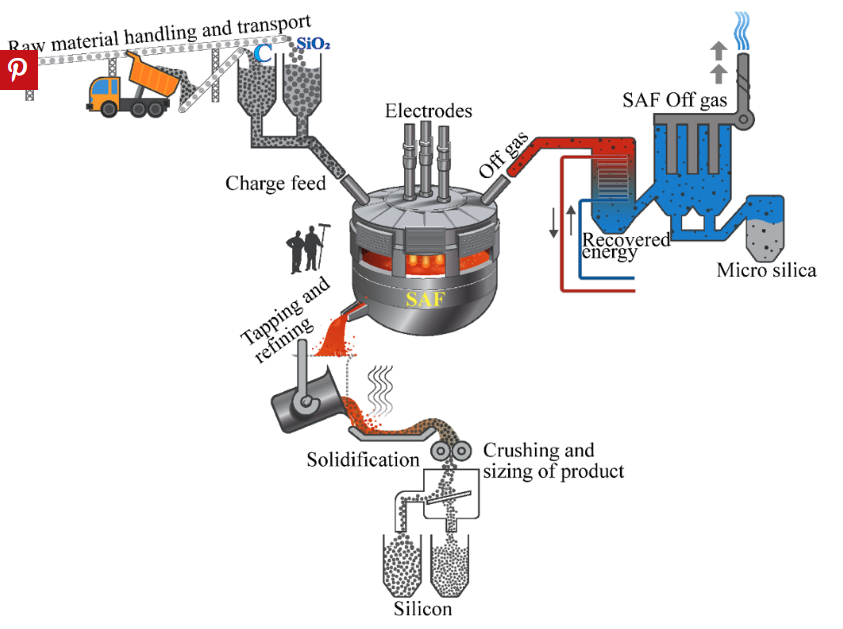
The primary raw material for silicon metal production is quartz, a form of high-purity silica (SiO2). Quartz is extracted from mines in the form of large rocks. These rocks are then transported to a processing plant where they are crushed into smaller pieces.
2. Reduction Process
The crushed quartz is mixed with a carbon source, typically coal, coke, or wood chips. This mixture is then fed into a submerged electric arc furnace. The furnace operates at extremely high temperatures, usually between 1,900°C and 2,400°C (3,452°F and 4,352°F).
In the furnace, a reduction reaction occurs:
This reaction reduces the silica in the quartz to silicon metal, releasing carbon monoxide gas as a byproduct.
3. Collection of Silicon Metal
As the silicon metal forms, it collects at the bottom of the furnace in a molten state. The molten silicon is periodically tapped from the furnace and allowed to cool and solidify. This raw silicon metal typically has a purity of about 98-99%, with impurities such as iron, aluminum, and calcium.
4. Refinement
To achieve higher purity levels, the raw silicon metal undergoes further refinement. One common method is the acid leaching process, where the silicon is treated with acids to remove impurities. Another method is zone refining, which involves melting a small region of a silicon rod and moving this molten zone along the rod. Impurities concentrate in the molten region and are moved to one end of the rod, which is then removed.
For electronic-grade silicon, the purity must be exceptionally high (99.9999% or higher). This is achieved through additional processes such as the Siemens process, which involves converting silicon into a volatile compound and then decomposing it back into pure silicon.
5. Final Product
The refined silicon metal is then cast into ingots or other shapes as required by the end users. These ingots can be further processed into silicon wafers for use in semiconductor devices or into polycrystalline silicon for solar panels.
6. Applications
Silicon metal produced through these processes is crucial for a wide range of applications:
- Electronics: High-purity silicon is the foundation for semiconductor devices, which are integral to all modern electronics.
- Solar Energy: Silicon is used to produce photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity.
- Aluminum Alloys: Silicon metal is added to aluminum to improve its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Chemical Industry: Silicon is used in the production of silicones, which are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, and various medical applications.
